

Description
CAS:1094-61-7;Assay:99% min
CAS NO.:1094-61-7
Brand:GSHWORLD
Glutathione bulk powder raw material - NMN suppliers & manufacturers in China.
Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) and is widely used to supplement NAD+.
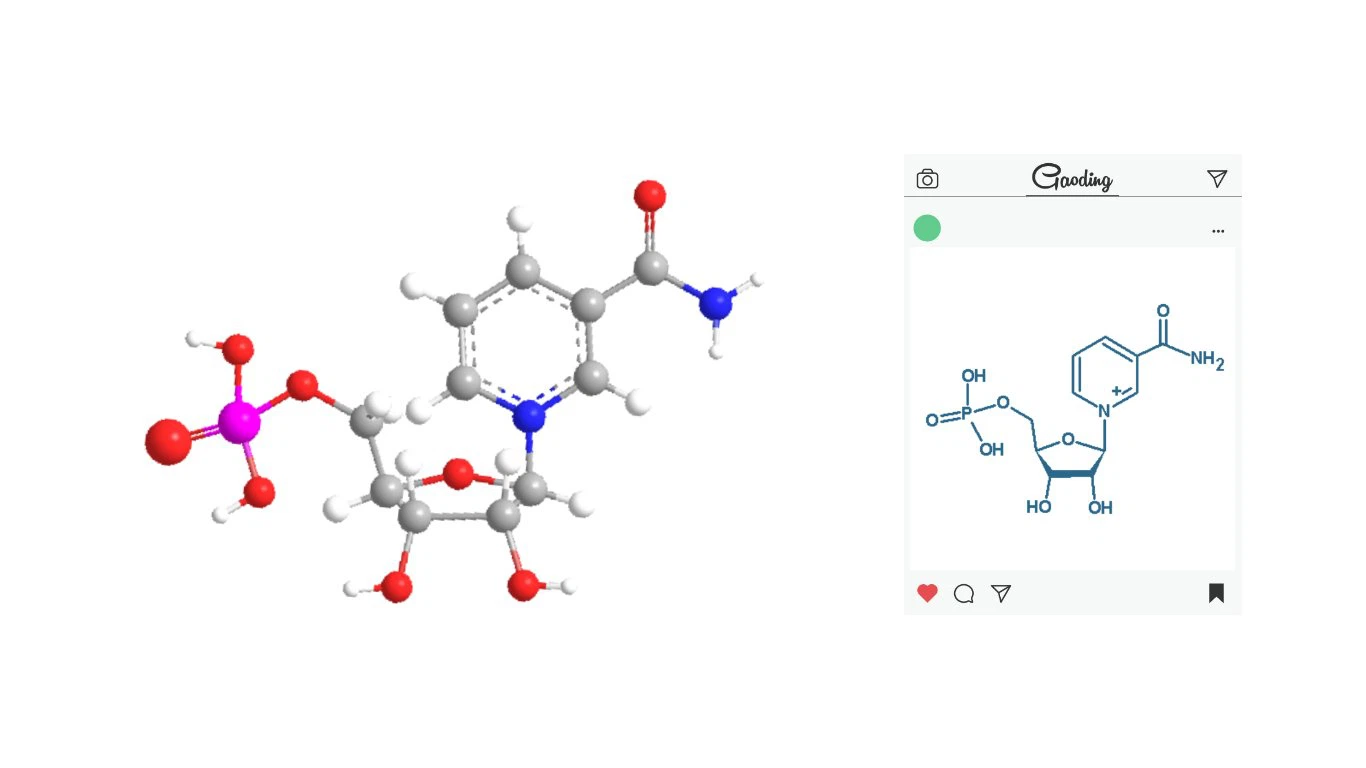
Bulk Powder Nicotinamide Mononucleotide(C11H15N2O8P) | |
CAS | 1094-61-7 |
Appearance | White or almost white powder |
Assay | 99% min |
Loss on drying | Not more than 0.5% |
Heavy Metal | Not more than 10ppm |
Chlorides | Not more than 200 ppm |
Sulfates | Not more than 300 ppm |
Iron | Not more than 20 ppm |
Arsenic | Not more than 1 ppm |
Bulk density | Not less than 0.15g/ml |
Shelf Life | Two years when properly stored. |
There is growing evidence that NAD+ supplementation can prevent bone loss. Studies have found that aluminum (Al) may cause bone damage, bone loss and oxidative stress. NMN treatment significantly attenuated Al-induced bone loss by reducing bone loss, inhibiting oxidative stress, and inhibiting the thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP)-NLRP3 inflammasome pathway and pro-inflammatory cytokine production in vivo and in vitro damage.
Nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase (Nampt), the rate-limiting enzymes for nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) synthesis, and the NAD+-dependent histone deacetylase Sirt1 protect the heart from ischemia/reperfusion (I /R). NMN significantly increased levels of NAD+ in the heart at baseline and prevented the decrease in NAD+ during ischemia. When NMN was administered 30 min before ischemia or 4 times before and during reperfusion, NMN protected the heart from I/R injury, suggesting that exogenous NMN could protect the heart from I/R injury during both ischemia and reperfusion phases I/R damage. The protective effect of NMN was accompanied by decreased acetylation of FoxO1, but not in Sirt1 KO mice, suggesting that the effect of NMN is mediated through activation of Sirt1. CR (60% calories) in mice significantly reduced I/R injury with concomitant Nampt upregulation compared to control diet (90% calories).
Studies have shown that decreased levels of cellular nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) contribute to aging-related diseases, and treatments that increase cellular NAD+ prevent these diseases in animal models. Administration of nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) has been shown to alleviate aging-related dysfunction. Plasma concentrations of N-methyl-2-pyridone-5-carboxamide and N-methyl-4-pyridone-5-carboxamide were significantly increased by NMN administration. In healthy men, a single oral dose of NMN is safe and effective and does not cause any apparent harmful effects. Therefore, oral NMN was found to be feasible, suggesting a potential therapeutic strategy to alleviate aging-related diseases in humans.
Notably, NMN did not have any apparent toxic or deleterious effects, NMN inhibited age-related weight gain, enhanced energy metabolism, promoted physical activity, improved insulin sensitivity and plasma lipid profile, and improved ocular function and other pathophysiology. NMN prevents age-related gene expression changes in key metabolic organs and enhances mitochondrial oxidative metabolism and mitochondrial protein imbalance in skeletal muscle.



+86-755-23577295
+86 18718790084
Room 832, Building 12, Shenzhen Bay Science and Technology Ecological Park, Yuehai Street, Nanshan District, Shenzhen China