
Oct 10, 2024 / Author: China Glutathione suppliers & NMN manufacturers
Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN), a naturally occurring substance in the human body, is involved in the synthesis of intracellular NAD+, and NAD+ is a key intracellular cofactor, widely involved in regulating important biological processes such as energy metabolism, oxidative damage and inflammatory response. With the increase of age, the level of NAD+ in the body gradually declines. This is closely related to many of the problems associated with aging.
As the precursor of NAD+, NMN can effectively improve the level of NAD+ in the body. As the "anti-aging star" of dietary supplements in recent years, NMN has been shown in many studies to help slow down the aging process of the ovary, but its molecular mechanism has not been deeply analyzed.
Fertility decline in older women is mainly manifested by ovulation dysfunction, chromosomal abnormalities in embryos, and increased risk of miscarriage.
Although the rapid development of assisted reproductive technology has helped to maintain fertility in older women, the aging of the ovaries with age, especially the decline in the quality of oocytes, remains a major challenge to healthy fertility.
As a key intracellular cofactor, NAD+ is widely involved in regulating important biological processes such as energy metabolism, oxidative damage and inflammatory response. With the increase of age, the level of NAD+ in the body gradually declines, which is closely related to many problems related to aging.
Niacinamide mononucleotide (NMN), as a precursor of NAD+, can effectively increase the level of NAD+ in the body and help to slow down the aging process of the ovary, providing a new possibility to deal with this challenge.
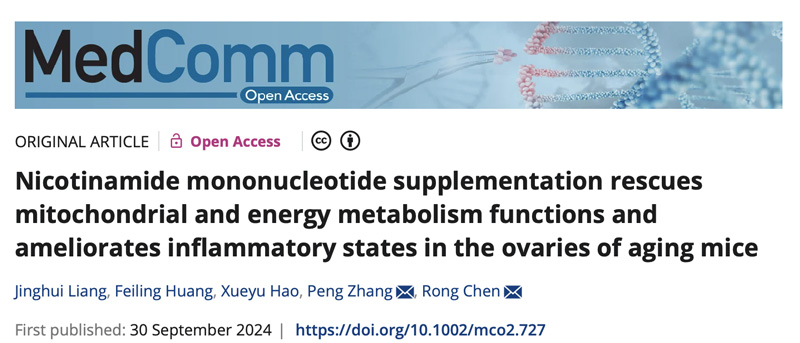
Recently, Professor Rong Chen's team from Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, together with Professor Peng Zhang's team from Children's National Medical Center/Beijing Children's Hospital Affiliated to Capital Medical University, published a paper entitled Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) in the journal MedComm. supplementation rescues mitochondrial and energy metabolism functions and ameliorates inflammatory states in the ovaries Research paper of aging mice.
This study reveals that NMN is a potential intervention that can significantly improve mitochondrial function and energy metabolism of the ovaries in aging mice, reduce the inflammatory state of the ovaries, and thus improve the health and reserve capacity of the ovaries.
The findings provide key insights into reproductive medicine to help develop more effective treatments to address the fertility challenges associated with ovarian aging.
In this study, the research team found that short-term NMN treatment can significantly increase the level of NAD+ in the ovaries of aging mice and the ratio of ovaries to body weight, and inhibit ovarian atrophy.
In the ovulatory stimulation experiment, NMN treatment significantly improved the quantity and quality of ovulatory stimulating cells in aging mice. These results suggest that NMN has good potential in inhibiting ovarian senescence.
The researchers further explored the effect and mechanism of long-term NMN treatment on ovarian aging, and found that NMN can improve serum hormone levels and antioxidant factors in aging mice, while reducing the expression of pro-inflammatory factors.
The number of ovarian follicles in aging mice increased significantly. Scanning electron microscopy showed that NMN treatment changed the morphology and distribution of lipid droplets and mitochondria in granulosa cells, revealing its potential mechanism of action.
Transcriptome sequencing and subsequent validation experiments showed that the positive effects of NMN on aging ovaries were achieved by enhancing mitochondrial function, improving energy metabolism, and reducing inflammation levels.
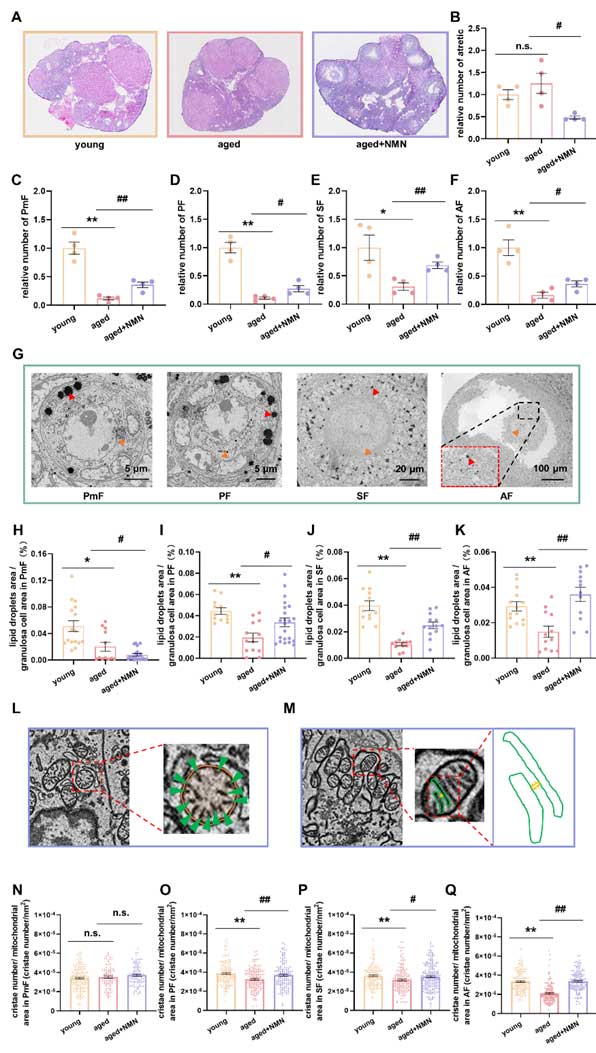
(A) representative pictures of HE staining in frozen sections of ovary of different groups of mice; (B-F) Statistical map of the number of follicles in the ovary at different developmental stages; (G) SEM representative images of follicles at different developmental stages of mouse ovaries; (H-K) Statistical maps of lipid droplet characteristics in follicular granulosa cells at different developmental stages; (L and M) Schematic diagram of statistical methods for mitochondrial parameters in mouse follicles; (N-Q) Statistical map of mitochondrial characteristics in follicles at different developmental stages.
These findings indicate that NMN supplementation can improve the aging state of the ovary and increase the reproductive reserve of the ovary, and its molecular mechanism is closely related to energy metabolism and inflammation levels involved in mitochondria, etc. This study provides a new idea for the mitigation and intervention of fertility decline in elderly women.
The team designed an experiment in which older mice were fed NMN to explore its potential effects on ovarian health. The experimental results showed that the intervention of NMN not only significantly increased the level of NAD+ in the elderly mice, but also effectively improved the overall condition of the ovary.
More exciting is that in the ovulation promotion experiment, the addition of NMN also promoted the number and quality of follicles in old mice to achieve double improvement. This finding not only proves the effectiveness of NMN in delaying ovarian aging, but also provides a solid theoretical basis for improving fertility in older women through scientific means.
In order to fully uncover the mechanism of action of NMN, the research team further explored its long-term impact on ovarian aging. Through a series of complex biochemical analyses and molecular biology experiments, they found that NMN was able to significantly enhance serum hormone secretion and antioxidant capacity in elderly mice, while reducing levels of inflammatory factors in the body. These changes act on ovarian tissue together, promote the formation and development of follicles, and thus realize the effective inhibition of ovarian senescence.
In particular, the research team also used advanced scanning electron microscopy technology to visually observe the changes in the morphology and structure of granular cells in ovarian cells by NMN. They found that NMN can optimize the distribution and morphology of lipid droplets and mitochondria in granulosa cells, thereby improving the metabolic efficiency and antioxidant capacity of the cells. This finding not only provides intuitive evidence support for the mechanism of NMN, but also opens up new ideas for subsequent related research.
After that, through the comprehensive application of advanced technical means such as transcriptome sequencing and experimental verification, the research team in-depth analyzed the specific role of NMN in ovarian protection. They found that NMN exerts its protective effect on the ovaries mainly through enhancing mitochondrial function, improving energy metabolism and reducing inflammation levels. This discovery not only enriches our understanding of the mechanism of ovarian aging, but also provides valuable clues and references for the development of novel treatments for the decline of fertility in elderly women.
Levels of NAD+, a key molecule in intracellular energy metabolism and DNA repair, gradually decline in the body with age, a process closely associated with multiple signs of aging, including a decline in ovarian function.
As a precursor of NAD+, NMN can effectively increase the level of NAD+ in the body, thereby enhancing the energy production efficiency of ovarian cells.
By improving mitochondrial function and energy metabolism, NMN helps ovarian cells better cope with oxidative stress and damage and maintain the normal function of the ovary.
Ovarian cells are vulnerable to free radical attack during aging, leading to cell damage and dysfunction.
NMN can enhance the antioxidant capacity of ovarian cells and reduce the damage of free radicals to cells, so as to protect the health of ovarian cells. This antioxidant effect helps slow the natural aging process of the ovaries.
As we age, there may be an inflammatory response within the ovaries, which can negatively affect ovarian function.
NMN can reduce the level of inflammation in the ovary, reduce the damage of inflammatory response to ovarian cells, and thus improve ovarian function. This anti-inflammatory effect helps maintain the normal physiological environment of the ovaries and promotes the normal development of follicles and ovulation.
Hormones secreted by the ovaries play an important role in maintaining female physiological function and fertility.
NMN can improve ovarian function by affecting the synthesis and secretion of ovarian hormones and regulating the balance of hormone levels.
This regulatory effect helps maintain a woman's normal menstrual cycle and fertility.
Supplier Introduction: China glutathione supplier and NMN manufacturer GSHworld, the company mainly develops biotechnology and industrialization. As a global pioneer in enzymatic catalytic ATP regeneration technology, our company advocates green production and is committed to providing customers with better and more environmentally friendly products and services. Glutathione Manufacturer,NMN Factory,Citicoline Sodium supplier,China NMN manufacturers
+86-755-23577295
+86 18718790084
Room 832, Building 12, Shenzhen Bay Science and Technology Ecological Park, Yuehai Street, Nanshan District, Shenzhen China